What You Need To Know
Skin cancer is the most common cancer in the United States and worldwide.
- 1 in 5 Americans will develop skin cancer by the age of 70.
- More than 2 people die of skin cancer in the U.S. every hour.
- Having 5 or more sunburns doubles your risk for melanoma.
- When detected early, the 5-year survival rate for melanoma is 99 percent.
Theres more than meets the eye when it comes to skin cancer, so make sure you know all the facts. You can #SharetheFacts on social media by downloading images from our Skin Cancer Awareness Toolkit. For the latest news, visit our Press Room.
Think Youre Not At Risk Because You Dont Have Fair Skin Think Again You Could Be More At Risk
If you have a darker skin tone and dont tend to burn as quickly or easily as other people, this is not a reason to let your guard down when it comes to sun protection. In fact, it may be a reason to be even more cautious.
Many think that because they have a certain skin type they arent at risk for skin cancer from a sunburn. Being aware that anyone can get skin cancer is important, Jaliman said.
As Min Deng, a dermatologist at MedStar Health, shared with HuffPost, skin cancers affect Black and Hispanic people at a disproportionately deadly rate compared to white people.
When skin cancer is found in Black and Hispanic people, they tend to be diagnosed at a later stage and, as a result, have a worse prognosis, Deng said.
What Causes Skin Cancer
Ultraviolet radiation from the sun is the number one cause of skin cancer, but UV light from tanning beds is just as harmful. Exposure to sunlight during the winter months puts you at the same risk as exposure during the summertime.
Cumulative sun exposure causes mainly basal cell and squamous cell skin cancer, while episodes of severe blistering sunburns, usually before age 18, can cause melanoma later in life. Other less common causes are repeated X-ray exposure, scars from burns or disease, and occupational exposure to certain chemicals.
Ultraviolet A and Ultraviolet B rays also affect the eyes and the skin around the eyes. Sun exposure may lead to cataracts, cancer of the eyelids, and possibly macular degeneration.
Read Also: Large Cell Carcinoma Lung Cancer
What Is The Treatment For Melanoma
Confirmed melanoma usually undergoes a second surgical procedure known as wide local excision. The clinical margins of this excision are dependent on the size and thickness of the melanoma . The Recommended New Zealand margins for excision of melanoma are as follows:
- Melanoma in situ: 510 mm
- Melanoma < 1 mm: 10 mm
- Melanoma 12 mm: 1020 mm
- Melanoma > 2 mm: 20 mm.
It is also important to determine the extent or stage of the melanoma and whether it has spread from the site of origin. The American Joint Committee on Cancer cutaneous melanoma staging guidelines are the commonly used staging criteria. The AJCC staging criteria for cutaneous melanoma are as follows :
- Stage 0: in situ melanoma
- Stage I: thin melanoma < 2 mm in thickness
- Stage II: thick melanoma > 2 mm in thickness
- Stage III: melanoma spread to involve local lymph nodes
- Stage IV: distant metastases have been detected.
Note: non-cutaneous forms of melanoma may have different staging criteria .
What Is Skin Cancer
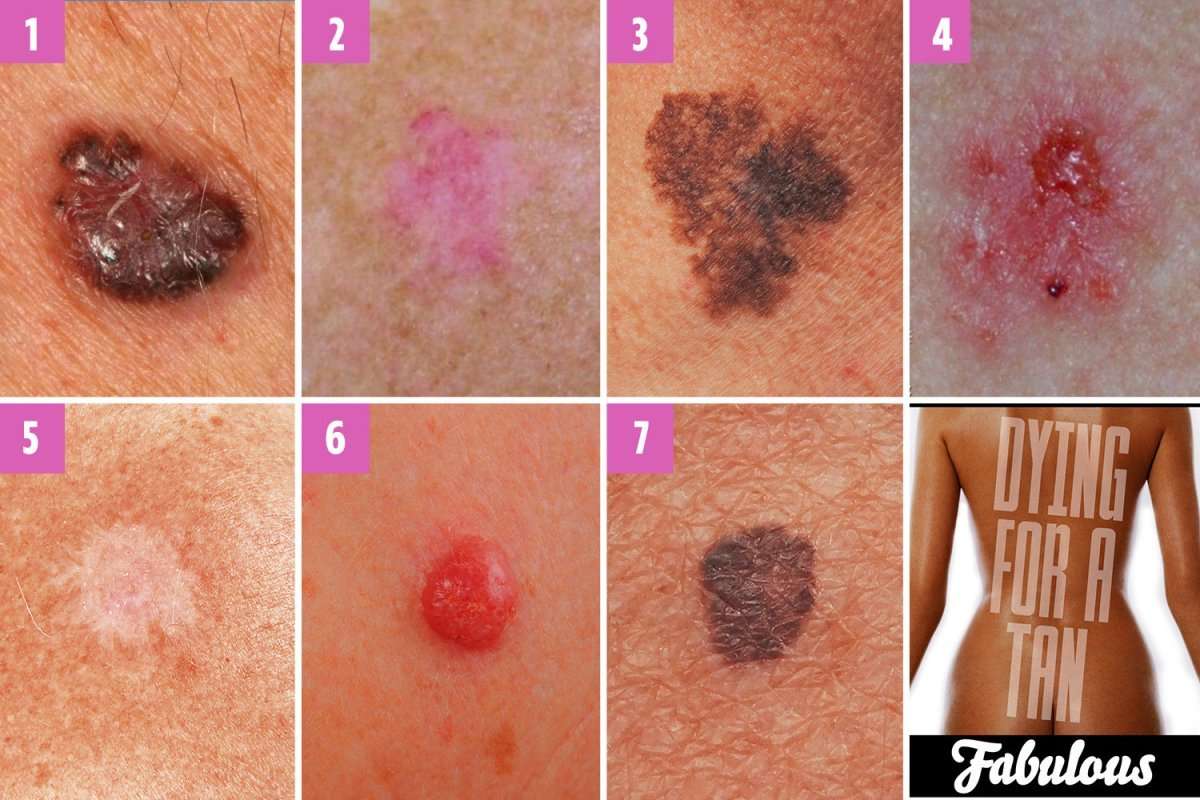
Skin cancer is the most common form of cancer in the US, and the number of cases continues to rise. It is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal skin cells. While healthy cells grow and divide in an orderly way, cancer cells grow and divide in a rapid, haphazard manner. This rapid growth results in tumors that are either benign or malignant .
There are three main types of skin cancer:
Basal cell and squamous cell cancers are less serious types and make up 95% of all skin cancers. Also referred to as non-melanoma skin cancers, they are highly curable when treated early.
Melanoma, made up of abnormal skin pigment cells called melanocytes, is the most serious form of skin cancer and causes 75% of all skin cancer deaths. Left untreated, it can spread to other organs and is difficult to control.
Don’t Miss: What Does Cancer Tissue Look Like
Dont Brush Off One Bad Burn
It bears repeating that just one bad sunburn can double your risk of getting a melanoma.
Sunburns should never be normalized, Jaliman explained, noting that if you have a family history of skin cancer, you should be extra cautious . Genetics play a role. Families tend to have similar skin types, which may increase your risk of developing a skin cancer if you have a strong family history of malignant melanomas.
If youre wondering about that afternoon you spent in the sun last weekend and the slight tinge of pink that appeared on your shoulders or face, its important to know that this, too, is risky.
Even getting pink from the sun indicates some damage at a cellular level, Fromowitz shared.
So Can Dark Skin Tones Still Sunburn
In short, yes. Darker skin tones originate in parts of the world closest to the equator where UV exposure is highest. Melanin absorbs and scatters UV energy in a similar fashion to sunscreen providing Fitzpatrick V and Fitzpatrick VI individuals with a baseline estimated SPF of 7-10. This natural SPF allows darker skin tones to better tolerate UV exposure and typically results in tanning without burning. However, darker skin tones can still develop sunburns with high sun exposure, use of treatments that make the skin more sensitive to the sun , and/or rapid changes in UV exposure (say, winter Caribbean vacations and/or beach time.
You May Like: What Type Of Skin Cancer Spreads The Fastest
What Are The Risks Associated With Skin Cancer In Black People
Due to the fact that skin cancer is less common in Black people, some may perceive their risk of skin cancer as low. They may not seek care for potentially cancerous skin changes.
A 2018 study used focus groups to evaluate Black and Latino peoples knowledge and attitudes about skin cancer. Researchers found that:
- Many study participants perceived themselves to have a low risk of skin cancer due to having a darker skin tone or a lack of family history of skin cancer.
- Black participants reported skin cancer symptoms more inconsistently than Latino participants.
- Few study participants reported regular use of sun protection behaviors.
Many times, skin cancer isnt diagnosed in Black people until its later stages. In fact, according to the American Academy of Dermatology, 25 percent of melanomas in Black people are diagnosed after the cancer has already spread to surrounding lymph nodes.
Receiving a diagnosis at a later stage can make skin cancer much harder to treat. It can also negatively impact outlook.
How Common Is Skin Cancer In People Of Different Races
Skin cancer is the most common cancer in the United States, but it isnt clear how much it affects different racial groups. According to a research paper from 2009, skin cancer makes up as much as 45% of all cancers in white people, 5% of all cancers in Hispanic people, 4% of all cancers in Asian people, and 2% of all cancers in Black people.
Skin cancer is becoming more and more commonly diagnosed in white people, but in Black people, the rate of skin cancer seems to be staying low. However, when skin cancer is diagnosed in people of color, the tumor is often bigger, more advanced, and deadlier.
Take squamous cell carcinomas, for example. This type of skin cancer is 10 times more likely to spread if it happens in Black people compared to in white people. Looking at melanoma , a study from 2017 that analyzed a database of patients from 1988 to 2011 found that 92% of white patients were alive 5 years after they were diagnosed compared to just 72% of African Americans.
We know that skin pigmentation provides some protection from cancer, which might partially explain the lower rate of skin cancer among people of color. But there is also a lack of awareness among providers and patients that can lead to delays in diagnosis or a diagnosis being overlooked.
Also Check: Well Differentiated Squamous Cell Carcinoma Stages
What Causes Skin Cancer In Black People
In general, skin cancer is caused by genetic changes that occur in the DNA of our cells. Sometimes, these changes can be harmful, causing cells to begin to grow and divide out of control.
UV radiation from the sun can cause damage to DNA. Because of this, frequent exposure to UV rays in the form of sunlight or UV lamps is associated with an increased risk of skin cancer.
However, not all types of skin cancer may be linked to sun exposure. Indeed, some skin cancers in Black people occur in areas that arent exposed to much sunlight, such as the soles of the feet, palms of the hands, and nails.
This type of skin cancer is called acral lentiginous melanoma . Some dermatologists have reported that ALM makes up 30 to 70 percent of melanomas seen in People of Color visiting their practice.
Doctors dont yet know what causes ALM. However, its believed that genetic factors may play a role.
Do Black People Need Sunscreen
Short answer: Yes.
One of the first things I ask my clients is, Do you wear sunscreen? and theyre always like, Oh no! I dont have to! Latoya Chaplin, a Black esthetician from Maryland who specializes in Black skin, told HuffPost. I think a lot of Black women believe that just because theyre not burning , theyre not getting sun damage.
There is a belief that Black skins melanin, the pigment that makes skin darker, naturally protects skin from the sun and its UV rays, creating a barrier against the negative effects of the sun. But as Dr. Sheel Desai Solomon, a dermatologist in Raleigh-Durham, North Carolina, explained, thats not necessarily the case.
An African American person has melanin that blocks UV light up to SPF 13, Solomon told HuffPost. This isnt as strong as the sunscreen which is created for skin protection. Yes, sunscreen is needed.
African American people often think that because they have more melanin that they have natural sunscreen.â That places them in grave danger.
â Dr. Sheel Desai Solomon
Theres been debate about whether sunscreen is more harmful than helpful, since the skin can absorb chemicals from sunscreen into the bloodstream. However, the FDA has not determined these chemicals to be unsafe and the agency still stresses the importance of wearing sunscreen in order to prevent other deadly diseases. Even in the winter, Solomon suggests putting on sunscreen to protect from UV radiation.
Recommended Reading: How Fast Does Squamous Cell Carcinoma Spread
Early Detection And Prevention
Many dermatologists do not have experience in treating people with darker skin. Implicit bias during assessment and diagnosis can also play a role, so it is important that Black people know the signs of skin cancer.
No matter what type of skin cancer a person has, detecting it early improves their outlook. Knowing the signs and symptoms of skin cancer can help a person detect suspicious skin growths early.
An individual can try :
- Doing regular skin checks every few months: When a person is familiar with their skin, it makes it easier to detect potentially harmful changes in moles and freckles.
- Visiting a dermatologist for an annual skin cancer screening: This is particularly important if a person has a family history of skin cancer.
- Wearing sunscreen in the sun: Black people can burn, too. The melanin in Black skin has an estimated
usually begins as a change in the skin. This can be a new growth like a freckle or a mole or changes to an existing growth.
Being familiar with their skin can help a person detect abnormalities. Regular skin self-exams can help a person get to know their skin and how their moles and freckles typically look.
When people find a questionable mole or freckle, they can wonder whether or not it may be melanoma. Try using the acronym ABCDE to check growths when doing a skin exam:
Diagnosing skin cancer starts with an exam. A doctor will use a scope to look at suspicious skin growths.
Can Melanoma Be Prevented

Most childhood types of melanoma can’t be prevented because they are due to a mutation .
The most important way to prevent melanoma from developing later in life is to limit kids’ and teens’ sun exposure.
Keep kids younger than 6 months out of the sun entirely, because their skin is so sensitive. If any skin must be exposed to the sun, use a small amount of sunscreen on those parts, such as the face and hands.
Kids 6 months and older should use sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 every day.
Other ways to help prevent skin cancer include:
- avoiding the strongest sun of the day, between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
- encouraging kids to wear wide-brimmed hats and long, loose cotton clothing, especially if they tend to burn easily
- making sure teens understand the dangers of tanning salons
- being a good role model yourself
Not all skin cancer is melanoma, but every case of melanoma is serious. Do what you can to lower your kids’ risk and help them make smart choices about sun safety.
You can find more information online at:
Don’t Miss: Stage 2 Carcinoma
More Sun Equals More Skin Cancer
April 14, 2000 — Just because you’re black, doesn’t mean you don’t need sunscreen. Skin cancer rates for blacks go up as their exposure to sunlight goes up, just as they do in whites, according to a study in the journal Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention.
“The study is a wake-up call for people with brown and black skin that may not protect you from skin cancer if you get a lot of sunlight,” A. Paul Kelly, MD, tells WebMD. Kelly is professor and chief of dermatology at the King/Drew Medical Center in Los Angeles.
Researchers were particularly concerned about the role of ultraviolet-B rays, the ones that cause skin cancer.
“This paper adds to the evidence that UVB radiation can increase the risks of skin cancer in the black population,” co-author Mitchell Gail, MD, PhD, tells WebMD. He is chief of the biostatistics branch at the National Cancer Institute’s Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics.
Co-author Susan Devesa, PhD, who is chief of the descriptive studies section of the biostatistics branch, says that black people vary widely in their degree of pigmentation and that light-skinned blacks, in particular, may benefit from using such preventive measures as sunscreen.
During those time periods, nearly 1,100 black men and more than 1,200 black women died of melanoma. More than 73,000 white men and almost 50,000 white women died of melanoma.
Treatment For Skin Cancer
For the most part, skin cancer is treated the same way indark-skinned people as it is in those with lighter skin.
It begins with surgery to remove the cancer. However, takingadditional precautions can reduce scarring in people with darker skin, as theytend to suffer from thick scars, known as keloids.
If a patient comes to me with basal cell carcinoma, whichis the most common type of skin cancer, I ask about any previous experiencewith scars, Dr. Kyei explains. The reason I ask that question is that I dontwant someone to end up with a thick scar somewhere noticeable like their face.If youre someone who tends to get thick keloids and your cancer is verysuperficial and not high-risk, we might start with a chemotherapy cream as aninitial treatment method instead of surgery.
Despite the potential for scarring, surgery is the onlytreatment method for melanoma. Melanoma is deadly, Dr. Kyei says. It has tobe cut out no matter what.
Injected steroids can sometimes help minimize scarring.
You May Like: Basal Cell Carcinoma Syndrome
Q: While All Types Of Skin Cancer Are Less Common In People Of Color Their Outcomes Are Dramatically Worse What Accounts For This Gap
Skin cancers are less prevalent in nonwhite racial ethnic groups, but when they occur, they tend to be diagnosed at a later stage and, as a result, have a worse prognosis. One study, for example, found an average five-year melanoma survival rate of only 67 percent in Black people versus 92 percent in white people. Another showed that late-stage melanoma diagnoses are more common in Hispanic and Black patients than in non-Hispanic white patients.
First, theres a lower public awareness overall of the risk of skin cancer among individuals of color. Second, from the perspective of health-care providers, theres often a lower index of suspicion for skin cancer in patients of color, because the chances of it actually are smaller. So these patients may be less likely to get regular, full-body skin exams. And third, the places on the body where skin cancers tend to occur in people of color are often in less sun-exposed, more out-of-the-way areas, which makes detection more difficult. For example, the most common location for melanoma in patients of color is the lower extremities the soles of the feet in particular.
Recommended Reading: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 3 Life Expectancy
Melanoma & Skin Of Color
Melanoma is the deadliest skin cancer and represents about 5% of all cancer diagnoses in the United States each year. While rates for many cancers are decreasing, new cases of melanoma are rising rapidly, especially among younger people. In fact, cases of melanoma have tripled in the last 30 years. And while People of Color are diagnosed with melanoma less often, they are up to four times more likely to be diagnosed with advanced melanoma and 1.5 times more likely to die from the disease.
To learn more about the risks of melanoma among people of color, tips for sun-safety and detection, and well as additional information on acral melanoma , please continue reading.
Yes, People of Color Can Get Melanoma
According to the American Cancer Society, the lifetime risk of developing melanoma is 1 in 1,000 for Blacks, 1 in 167 for Hispanics, and 1 in 38 for whites.1 While the chance of developing melanoma among People of Color is less than among whites, melanoma does occur across all races. The idea that People of Color do not get melanoma is a myth and stands in the way of raising awareness of melanoma, and other skin cancers, among People of Color.
Melanoma May Look Different Among People of Color
Cutaneous melanoma, the most common type, is caused by cell damage from ultraviolet light from the sun. People of Color are far less likely to develop this type of melanoma than their white counterparts.2
Melanoma is Found Later Among People of Color
Later Diagnosis = Lower Survival
Read Also: Ductal Breast Cancer Survival Rates