Is Sun Exposure The Only Cause Of Skin Cancer
Skin cancer is one of the most common and treatable forms of cancer when caught in the early stages. Any person can develop skin cancer, but the cause depends on the type of cancer diagnosed as well as the persons skin type. People with lighter colored hair, eyes, and skin have a greater risk of developing skin cancer because their body contains less melanin that protects them from sun damage. Continuous exposure to the sun without the protection of sunscreen, hats, lightweight long-sleeved clothing, and other barriers increase the risk of developing skin cancer as well.
Although long-term, unprotected sun exposure is a leading cause of skin cancer, its not the only cause. It depends largely on whether a doctor diagnoses a non-melanoma or melanoma type of skin cancer.
If You Have One Of The Two Types Of Non
- A sore that crusts, bleeds, or oozes without scabbing over and healing for a period of several weeks
- One patch of skin appears tight and shiny like a scar
- A red, raised patch with or without itching
- A dip in the skin with a raised border
- A shiny, pearl-like bump
The terms basal cell and squamous cell refer to the layer of the skin where a doctor diagnoses a carcinoma, which means the skin contains cancer cells. Basal cell skin cancer means that cancer is present in the skins epidermis. Squamous cell skin cancer resides in the skins subcutaneous layer.
When Melanoma Can’t Be Cured
If your cancer has spread and it is not possible to cure it by surgery, your doctor may still recommend treatment. In this case, treatment may help to relieve symptoms, might make you feel better and may allow you to live longer.
Whether or not you choose to have anti-cancer treatment, symptoms can still be controlled. For example, if you have pain, there are effective treatments for this.
General practitioners, specialists and palliative care teams in hospitals all play important roles in helping people with cancer.
You May Like: Invasive Lobular Carcinoma Grade 2 Survival Rates
Types Of Skin Malignancies:
- Melanoma the least common form of skin cancer, but responsible for more deaths per year than squamous cell and basal cell skin cancers combined. Melanoma is also more likely to spread and may be harder to control.
- Nonmelanoma malignancies:
- Squamous cell cancer the second-most common skin cancer. It’s more aggressive and may require extensive surgery, depending on location and nerve involvement.
- Basal cell cancer the most common form of skin cancer. It is rarely fatal but can be locally aggressive.
These skin malignancies are typically caused by ultraviolet radiation from exposure to the sun and tanning beds.
Other Factors That Can Lead To Increased Risk Include Sunburns
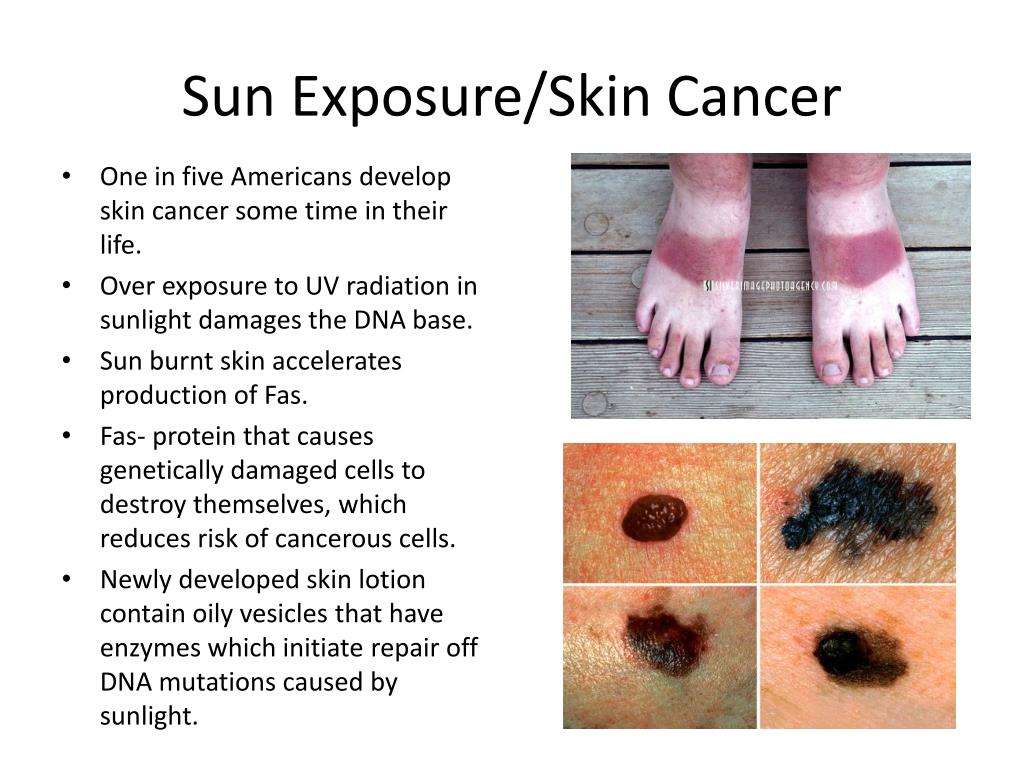
Sun damage is a serious issue, so its important to understand the different factors that can lead to increased risk. Sunburns are one of these factors, but theyre not the only ones. Repeated exposure to sunlight over many years and prolonged use of tanning beds also increase your chances of developing skin cancer or other harmful conditions like premature aging. The more you know about how sun damage works about your lifestyle choices, the better equipped youll be at taking care of yourself while avoiding damaging effects on your health and appearance.
Read Also: Cancer All Over Body Symptoms
Using The Sun To Your Advantage
The key principle in healthy sun exposure is to spend as much time in the sun as you can and never get burned. If you have light skin, this may be only 10-20 minutes during peak UVB hours . If you have darker skin, it may take your body some time to reach peak vitamin D production.
Sunscreen and long-sleeved clothing can stop the rays in their tracks, so make sure to give the sun some real estate by exposing your arms and/or shoulders while outside. If youre going to be outside for long period of time, soak up the sun for a bit and cover up or apply some homemade sunscreen to protect your skin from burning.
Risk Of Getting Melanoma
Melanoma is more than 20 times more common in whites than in African Americans. Overall, the lifetime risk of getting melanoma is about 2.6% for whites, 0.1% for Blacks, and 0.6% for Hispanics. The risk for each person can be affected by a number of different factors, which are described in Risk Factors for Melanoma Skin Cancer.
Melanoma is more common in men overall, but before age 50 the rates are higher in women than in men.
The risk of melanoma increases as people age. The average age of people when it is diagnosed is 65. But melanoma is not uncommon even among those younger than 30. In fact, its one of the most common cancers in young adults .
Read Also: Basal Cell Carcinoma Etiology
Myth : When It Comes To Sunscreen The Higher The Spf The Better
SPF protection doesnt increase proportionately with the designated SPF number. SPF 30 absorbs 97% of the suns burning UV rays, while SPF 50 absorbs just slightly more 98%. And, SPF 100 absorbs 99%. So, choose a sunscreen with at least an SPF 30.
A higher SPF does give you a little extra protection, but it’s still not a perfect block, especially in the real world where we all tend to apply too little and not reapply, George says. “Your best protection is to stay out of the sun, especially between the peak hours of 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., and to wear protective clothing if you have to be in the sun.”
What Age Does Skin Cancer Commonly Develop
The older you get, the higher your chance for developing skin cancer. About half of all Americans will develop either BCC or SCC at least once by the time theyre 65. The average age of a melanoma diagnosis is 63 , notes the American Cancer Society.
But melanoma is also one of the most frequently occurring cancers in young adults, especially women. Overall, melanoma occurs more frequently in women than in men before age 50. By age 65, twice as many men than women have melanoma. Rates triple by age 80.
Long-term exposure to the suns UV rays increases a persons chances of developing skin cancer. Artificial UV light, as found in indoor tanning beds, is also a culprit. It accounts for approximately of skin cancer each year in the United States, estimates a 2014 review and meta-analysis.
The Skin Cancer Foundation goes on to report that indoor tanning beds
- 0.10 percent for African-Americans
In their lifetime, 1 in 27 white men and 1 in 42 white women will develop melanoma, says the Skin Cancer Foundation .
While skin cancer is more common in white people, this population also has the best rate of survival. People of Hispanic, Asian, Native American, Pacific Islander, and African descent follow.
The of melanoma for white people with skin cancer is 94 percent, compared to only 69 percent survival in black people, notes the American Cancer Society.
Other reasons for the discrepancy include that nearly say they werent trained on diagnosing cancer on black skin.
Don’t Miss: Non Invasive Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Diagnosis Of Skin Cancer
It is important to check your skin regularly and check with your doctor if you notice any changes.
In the majority of cases, your GP will examine you, paying attention to any spots that may look suspicious. Your GP may perform a biopsy . In some cases your GP may refer you to a specialist, such as a dermatologist, if necessary.
Determine Your Skin Cancer Risk
The guidelines above apply to everyone, but certain individuals are at a higher risk for developing skin cancer and should be especially cautious with sun exposure.
If any of the descriptions below apply to you, see a dermatologist for a full-body examination once a year. Skin cancer risk is cumulative. The more risk factors you have and the more sun damage over a lifetime the higher your risk.
Skin cancer risk factors include:
- Personal history of skin cancer or precancerous skin lesions
- Tendency to freckle or burn easily
- Lots of sun exposure throughout your life
- Many sunburns as a child or adolescent
- Family history of skin cancer or conditions that are more likely to develop into skin cancer, such as dysplastic nevus syndrome or numerous atypical moles
- Chronic, non-healing wounds or burn injuries
- Radiation therapy
- Exposure to toxic materials, such as arsenic
- Exposure to certain subtypes of human papilloma virus . HPV 6,11,16 and 18 have been linked to the development of squamous cell carcinoma, especially in patients with compromised immune systems.
- Organ transplant patients on immunosuppressant drugs have an increased risk of skin cancer
Don’t Miss: What Does Cancer Look Like Outside The Body
Skin Cancer Of The Head And Neck Treatment
Many early-stage small basal cell cancers or squamous cell cancers can be removed by Mohs surgery, a technique that spares normal tissue through repeated intraoperative margin testing, removing only the cancer and leaving adjacent normal tissue. Tumors with nerve involvement, lymph node involvement or of a large size are not suitable for Mohs surgery. They require a multimodality approach to treatment, with formal surgical resection and adjuvant radiation or chemotherapy.
Melanoma is more likely to spread, and aggressive surgical resection with wide margins is required, in addition to radiation and/or chemotherapy.
Johns Hopkins Head and Neck Cancer Surgery
Johns Hopkins Head and Neck Cancer Surgery provides comprehensive surgical care and treatment for head and neck cancers. Our surgeons are at the leading edge of head and neck cancer treatment. You will benefit from the skilled care of head and neck surgeons, guiding clinical advancements in the field of head and neck cancer care.
What Changes In The Skin Occur Due To Exposure To The Sun
Exposure to sun causes most of the wrinkles and age spots on our faces. People think a glowing complexion means good health, but skin color obtained from being in the sun can actually speed up the effects of aging and increase the risk of developing skin cancer.
Sun exposure causes most of the skin changes that we think of as a normal part of aging. Over time, the sun’s ultraviolet light damages the fibers in the skin called elastin. When these fibers break down, the skin begins to sag, stretch, and lose its ability to go back into place after stretching. The skin also bruises and tears more easily in addition to taking longer to heal. So while sun damage to the skin may not be apparent when you’re young, it will definitely show later in life. The sun can also cause issues for your eyes, eyelids, and the skin around the eyes.
Changes in the skin related to sun exposure:
- Precancerous and cancerous skin lesions caused by loss of the skin’s immune function.
- Benign tumors.
- Fine and coarse wrinkles.
- Freckles discolored areas of the skin, called mottled pigmentation and sallowness, yellow discoloration of the skin.
- Telangiectasias, the dilation of small blood vessels under the skin.
- Elastosis, the destruction of the elastic tissue causing lines and wrinkles.
Read Also: Web Md Skin Cancers
Are There Different Types Of Radiation In Sunlight
Yes. The types of radiation include:
- visible light, which gives us the colours we see
- infrared radiation which gives us the warmth we feel
- ultraviolet radiation
Except in extreme situations, neither visible light nor infrared radiation from sunlight causes health problems. However, ultraviolet radiation can cause harmful effects to the skin.
There are three basic types of ultraviolet radiation:
- UVA
Table 1 summarizes the general features of each type.
| Table 1 Types of Ultraviolet Radiation and Their Features | |
|---|---|
| Ultraviolet Radiation Type | |
| Ultraviolet A radiation UVA, long-wave UV) | -not filtered out in the atmosphere -passes through glass -once considered harmless but now believed harmful over the long term -levels remain relatively constant throughout the day |
| Ultraviolet B radiation | -some filtered out in the atmosphere by the ozone layer -does not pass through glass -causes sunburn, tanning, wrinkling, aging of the skin and skin cancer -highest intensity at noontime |
| -filtered out in the atmosphere by the ozone layer before reaching earth -major artificial sources are germicidal lamps -burns the skin and causes skin cancer |
Basal Cell Carcinoma Pictures
Basal cell carcinoma usually appears in areas of the skin previously exposed to high levels of UV radiation such as the head, neck, ears and the back of the arms and hands. It is common in exposed skin of outdoor workers or people who have used sun tanning beds in the past.
As the basal cell carcinoma pictures below indicate, this type of skin cancer usually shows as a fleshy coloured bump that does not disappear over time and tends to grow slowly in size, eventually breaking down and ulcerating.
Below are pictures of skin cancer on the neck, face and trunk . These images show common areas where basal cell carcinoma develops, but it can develop anywhere.
Basal cell carcinoma. The skin cancer pictures in this article were licensed from DermNet NZ
Recommended Reading: Basaloid Tumor
Can Skin Cancer Be Prevented
Skin cancer is almost entirely preventable. Making a part of your life, avoiding sunburn, and checking your skin regularly will help prevent further damage to your skin.
Protect your skin from UV radiation and help prevent skin cancer by:
- slipping on sun-protective clothing: cover your shoulders, neck, arms, legs and body.
- slopping on sunscreen thats rated SPF 30+ or higher, broad-spectrum and water resistant.
- slapping on a hat that shades your face, neck and ears.
- seeking shade under trees, umbrellas and buildings from direct sunlight and reflective surfaces.
- sliding on sunglasses that wrap around your face to protect your eyes and surrounding skin.
- staying away from sun lamps, solariums or sunbeds, which emit dangerous levels of UV radiation.
UV radiation from the sun varies depending on time of day, season, where you live and cloud coverage. Protect your skin whenever UV Index levels are above 3. Use Cancer Council Australias free SunSmart app to check the UV Index for your area any time.
Most Australians will get enough vitamin D even with sun protection at UV level 3 or above. Babies and children should be protected from the sun, since they are particularly vulnerable to UV radiation harm.
While using fake tanning cream isnt harmful to your skin, it offers no protection from UV radiation. You still need to protect yourself from the sun.
Skin Cancer On The Rise
Melanoma, the most deadliest form of skin cancer, has steadily increased over the last few decades. According to the National Cancer Institute, the rate of new melanoma cases among American adults has tripled since the 1970s, from 7.9 per 100,000 people in 1975, to 23 per 100,000 in 2015 .
Each year, since 2003, rates of new melanoma cases have been climbing by around 1.7 percent for men and 1.4 percent for women each year . As a result, sun-care products have been thriving. But is there a correlation between skin cancer rise and the chemical ingredients in sunscreen? Does sunscreen cause cancer in those who are oblivious to the chemicals theyre putting on their skin?
The two most common kinds of skin cancer are basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, which are sometimes called non-melanoma skin cancer . Basal cell carcinomas account for more than 90 percent of all skin cancers in the United States, and is the most common of all cancers. Basal cell carcinomas are slow-growing and they very rarely spread to other parts of the body. Squamous cell carcinoma also rarely spreads, but it does so more often than basal cell carcinoma.
Then there is melanoma, a highly aggressive cancer that tends to spread to other parts of the body. These cancers may be fatal if not treated early .
You May Like: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 3 Life Expectancy
Does Sunscreen Cause Cancer
I dont know about you, but I read every ingredient on every product Im about to put on my skin. After all, our skin is the largest organ in our body, and science has long shown that what we put on our skin ends up in our bodies and quickly at that.
Many studies have demonstrated the effects of different sunscreens and how quickly the ingredients penetrate and absorb into the skin after application. One study, conducted in my home town at the Faculty of Pharmacy at the University of Manitoba, Canada, sought to develop a method for quantifying common sunscreen agents. Results revealed significant penetration of all sunscreen agents into the skin, meaning that all of these chemicals are entering our bloodstream, and as a result, entering multiple organs and cells within the body .
So, the next question becomes, are these ingredients that are entering our bloodstream particularly harmful? While much of the corporately-funded science that profits off the sales of sunscreen products says no, much of the unbiased research says yes.
The Food and Drug Administration hasnt reviewed the safety of these chemicals since the late 1970s. However, the Danish EPA concluded that after a careful review of the safety of active ingredients in sunscreen, most ingredients lacked information to ensure their safety . Sixteen of the 19 ingredients studied had no information about their potential to cause cancer.
Oxybenzone
According to the Environmental Working Group :
Methylisothiazolinone
Does Sunlight Cause Skin Cancer
There is evidence that sunlight causes skin cancer. Skin cancer can be treated and cured without serious consequences. However, in some cases the condition can be life-threatening if not diagnosed in time.
Skin cancer is an occupational concern for people who work under the sun. The risk however, may be reduced through awareness of the problem, and by taking measures to prevent exposure to sunlight.
Read Also: What Does Melanoma In Situ Look Like