How Can People With Dark Skin Get Skin Cancer
Although dark skin does not burn in the sun as easily as fair skin, everyone is at risk for skin cancer. Even people who don’t burn are at risk for skin cancer. It doesn’t matter whether you consider your skin light, dark, or somewhere in between. You are at risk for skin cancer. Being in the sun can damage your skin. Sunlight causes damage through ultraviolet, or UV rays, . Two parts of UV, UVA and UVB, can both cause damage to skin. Also, the sun isn’t the only cause of skin cancer. There are other causes. That’s why skin cancer may be found in places on the body never exposed to the sun.
How The Government Of Canada Protects You
The Public Health Agency of Canada monitors cancer in Canada. PHAC identifies trends and risk factors for cancer, develops programs to reduce cancer risks, and researches to evaluate risks from the environment and human behaviours. Health Canada also promotes public awareness about sun safety and the harmful effects of UV rays.
How Can I Protect Myself From Skin Cancer
Have your doctor check your skin if you are concerned about a change.Your doctor may take a sample of your skin to check for cancer cells.
Ask your doctor about your risk of skin cancer:
- Some skin conditions and certain medicines may make your skin more sensitive to damage from the sun.
- Medicines or medical conditions that suppress the immune system may make you more likely to develop skin cancer.
- Having scars or skin ulcers increases your risk.
- Exposure to a high level of arsenic increases your risk.
Stay out of the sun as much as you can. Whenever possible, avoid exposure to the sun from10 a.m. to 4 p.m. If you work or play outside, then
- Try to wear long sleeves, long pants, and a hat that shades your face, ears, and neck with a brim all around.
- Use sunscreen with a label that says it is broad spectrum or is at least SPF 15 and can filter both UVA and UVB rays.
- Wear sunglasses that filter UV to protect your eyes and the skin around your eyes.
- If you are concerned about having a low level of vitamin D from not being in the sun, talk with your doctor about supplements.
Don’t use tanning beds, tanning booths, or sunlamps.
Related Resources
You May Like: What Do Skin Cancer Sores Look Like
How Is Skin Cancer In Children Treated
Skin cancer in children and adults is categorized by stages 0 through 4. The more advanced a cancer is, the higher its stage. Treatment options depend on the stage and location of the cancer.
Stage 0 or 1 melanoma can usually be treated successfully with wide excision, an operation that removes the mole and the healthy skin just around its margins.
At stage 0, a melanoma may instead be treatable with imiquimod cream , a prescription ointment that helps cancerous and noncancerous skin growths disappear.
Stage 2 melanoma requires wide excision, and may also involve a lymph node biopsy. A stage 2 melanoma may have invaded the lymph system, so a biopsy may be appropriate. Talk with your childs doctor about whether a biopsy makes sense at this stage.
Stage 3 melanoma requires surgery to remove the tumor and surgery on the lymph nodes to which the cancer spread. Radiation therapy may also be necessary.
Stage 4 melanoma can be very difficult to treat. This stage means the cancer has spread to distant lymph nodes and possibly other parts of the body. Surgery, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy may all be involved.
What Causes Skin Cancer In A Child
Exposure to sunlight is the main factor for skin cancer. Skin cancer is more common in people with light skin, light-colored eyes, and blond or red hair. Other risk factors include:
-
Age. Your risk goes up as you get older.
-
Family history of skin cancer
-
Having skin cancer in the past
-
Time spent in the sun
-
Using tanning beds or lamps
-
History of sunburns
-
Having atypical moles . These large, oddly shaped moles run in families.
-
Radiation therapy in the past
-
Taking a medicine that suppresses the immune system
-
Certain rare, inherited conditions such as basal cell nevus syndrome or xeroderma pigmentosum
-
HPV infection
-
Actinic keratoses or Bowen disease. These are rough or scaly red or brown patches on the skin.
Also Check: What Can Happen If Skin Cancer Is Left Untreated
Who Is At Risk For Skin Cancer
Although anyone can get skin cancer, the risk is greatest in people who have fair or freckled skin that burns easily, light eyes and blond or red hair. Darker-skinned individuals are also susceptible to all types of skin cancer, although their risk is lower.
In addition to complexion, other risk factors include having a family history or personal history of skin cancer, having an outdoor job, and living in a sunny climate. A history of severe sunburns and an abundance of large and irregularly shaped moles are risk factors unique to melanoma.
What Changes In The Skin Occur Due To Exposure To The Sun
Exposure to sun causes most of the wrinkles and age spots on our faces. People think a glowing complexion means good health, but skin color obtained from being in the sun can actually speed up the effects of aging and increase the risk of developing skin cancer.
Sun exposure causes most of the skin changes that we think of as a normal part of aging. Over time, the sun’s ultraviolet light damages the fibers in the skin called elastin. When these fibers break down, the skin begins to sag, stretch, and lose its ability to go back into place after stretching. The skin also bruises and tears more easily in addition to taking longer to heal. So while sun damage to the skin may not be apparent when you’re young, it will definitely show later in life. The sun can also cause issues for your eyes, eyelids, and the skin around the eyes.
Changes in the skin related to sun exposure:
- Precancerous and cancerous skin lesions caused by loss of the skin’s immune function.
- Benign tumors.
- Fine and coarse wrinkles.
- Freckles discolored areas of the skin, called mottled pigmentation and sallowness, yellow discoloration of the skin.
- Telangiectasias, the dilation of small blood vessels under the skin.
- Elastosis, the destruction of the elastic tissue causing lines and wrinkles.
You May Like: How Is Skin Cancer Detected And Diagnosed
Soft Tissue And Bone Cancers
Sarcomas are cancers that start in connective tissues such as muscles, bones, or fat cells. There are 2 main types of sarcoma:
- Soft tissue sarcomas
- Bone sarcomas
Sarcomas can develop at any age, but some types occur most often in older teens and young adults.
Soft tissue sarcomas: These cancers can start in any part of the body, but they often develop in the arms or legs. Rhabdomyosarcoma, a cancer that starts in cells that normally develop into skeletal muscles, is most common in children younger than 10, but it can also develop in teens and young adults. Most other types of soft tissue sarcomas become more common as people age. Symptoms depend on where the sarcoma starts, and can include lumps , swelling, or bowel problems.
For more information, see Soft Tissue Sarcoma and Rhabdomyosarcoma.
Bone sarcomas: The 2 most common types of bone cancer,osteosarcoma and Ewing sarcoma, are most common in teens, but they can also develop in young adults. They often cause bone pain that gets worse at night or with activity. They can also cause swelling in the area around the bone.
Osteosarcoma usually starts near the ends of the leg or arm bones. The most common places for Ewing sarcoma to start are the pelvic bones, the bones of the chest wall , or in the middle of the leg bones.
For more information, see Osteosarcoma and Ewing Family of Tumors.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Skin Cancer
The most common warning sign of skin cancer is a change on the skin, typically a new mole, a new skin lesion or a change in an existing mole.
- Basal cell carcinoma may appear as a small, smooth, pearly, or waxy bump on the face, or neck, or as a flat, pink/red- or brown-colored lesion on the trunk, arms or legs.
- Squamous cell carcinoma can appear as a firm, red nodule, or as a rough, scaly, flat lesion that may itch, bleed and become crusty. Both basal cell and squamous cell cancers mainly occur on areas of the skin frequently exposed to the sun, but can occur anywhere.
- Melanoma usually appears as a pigmented patch or bump. It may resemble a normal mole, but usually has a more irregular appearance.
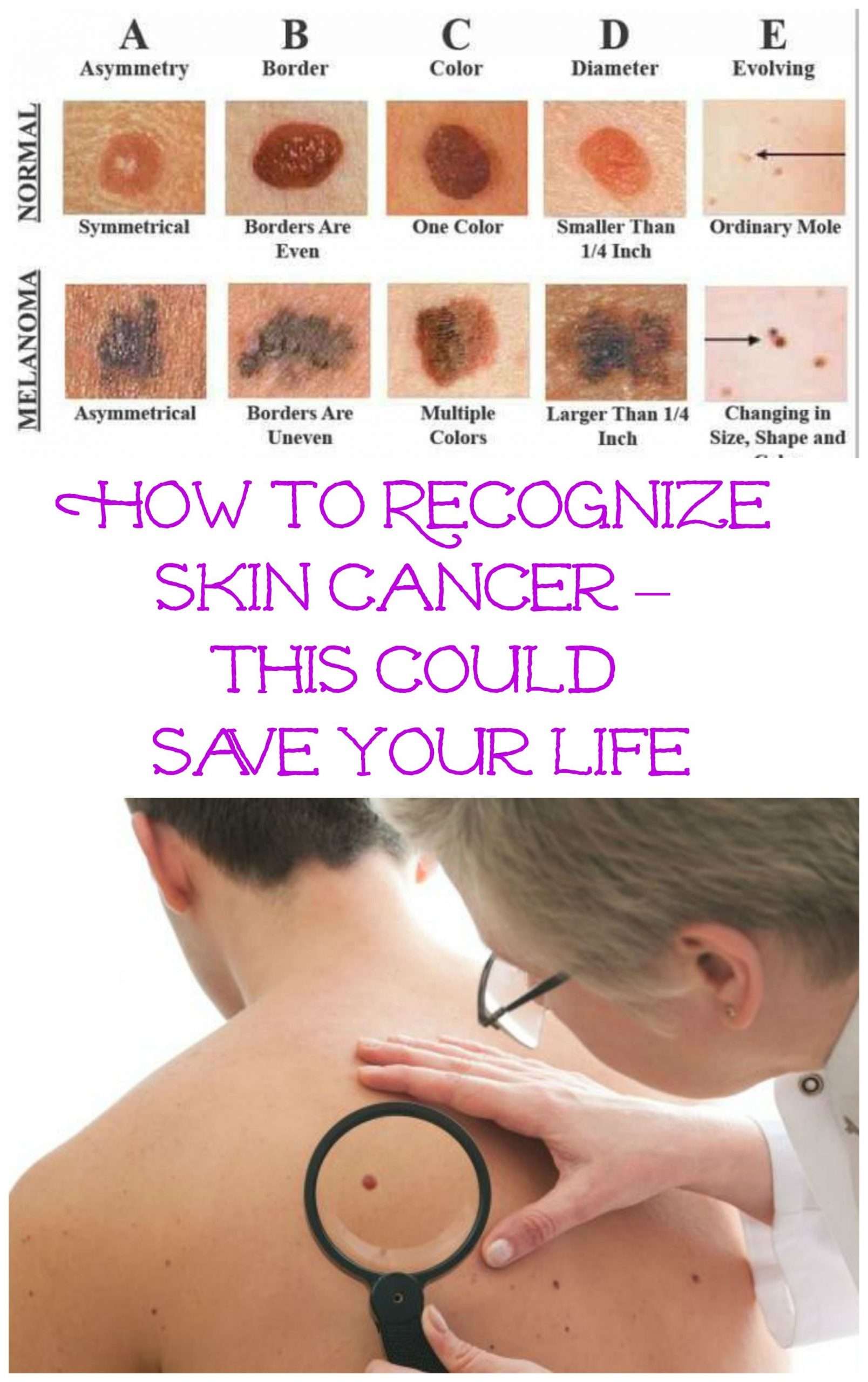
When looking for melanoma, think of the ABCDE rule that tells you the signs to watch for:
- Asymmetry: The shape of one half doesn’t match the other.
- Border: Edges are ragged or blurred.
- Color: Uneven shades of brown, black, tan, red, white or blue.
- Diameter: A significant change in size .
- Evolution: Changes in the way a mole or lesion looks or feels .
Also Check: What Does Stage 2 Melanoma Look Like
Skin Cancer: Young Adults Get It Too
Editor’s note: Updated June 3, 2015, to add new research presented at the American Society for Clinical Oncology meeting and CDC report on melanoma.
At 27, just months after Danielle got married, she gave in to her husband Derekâs pleas to get a troublesome mole on her stomach checked out. The mole had been there for years, and her family was also concerned about it. “It would peel off and flake off and bleed,” she says.
Her doctor diagnosed her with the most deadly of skin cancers: melanoma. Even worse, it had spread to her lymph nodes. “Our first year of marriage was spent in hospitals, doctors’ offices, The Cancer Center, at chemo treatments, and having numerous surgeries,” she says.
Sheâs now in remission, but she has to go back to her oncologist every 3 months and to her doctor for skin checks every 6 months.
“You always think it can’t happen to you, but it does,” says Danielle, now 29. “I wish someone had told me when I was younger that tanning is not cute.”
Can Melanoma Be Prevented
You can’t control how fair your skin is or whether you have a relative with cancerous moles. But there are things you can do to lower your risk of developing melanoma. The most important is limiting your exposure to the sun.
Take these precautions:
- Avoid the strongest sun of the day between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
- Use broad-spectrum sunscreen whenever you’re in the sun.
- Wear a wide-brimmed hat and cover up with long, loose cotton clothing if you burn easily.
- Stay out of the tanning salon. Even one indoor tanning session increases your risk of getting melanoma.
Also, be sure to check your moles often . Keep dated records of each mole’s location, size, shape, and color, and get anything suspicious checked out right away.
Not all skin cancer is melanoma, but every case of melanoma is serious. So now that you know more about it, take responsibility for protecting yourself and do what you can to lower your risk.
You can find more information online at:
Don’t Miss: How Do You Remove Skin Cancer
What Is The Outlook For Skin Cancer In Children
Skin cancer in children is on the rise. Theres been an increase in awareness of the dangers of too much UV exposure and the importance of skin cancer screenings. Teach your child how to check for suspicious moles, sores, and growths, and schedule annual visits with your pediatrician.
If your child is at higher risk for melanoma or you or your pediatrician notice any suspicious lesions, have your child see a dermatologist. This will help you catch pediatric melanoma or any other type of skin cancer in children at its earliest, most treatable stage.
Treating early-stage melanoma is usually successful. Surgery may leave little or no scar if the melanoma is diagnosed when its still small.
Stay Away From Tobacco

There is no safe form of tobacco. If you smoke cigarettes or use other types of tobacco products, it’s best to stop. It’s also important to stay away from tobacco smoke . Both using tobacco products and being exposed to tobacco smoke can cause cancer as well as many other health problems. If you don’t use tobacco products, you can help others by encouraging the people around you to quit. Call us at 1-800-227-2345 for help, or see How to Quit Smoking or Smokeless Tobacco to learn more about quitting.
Read Also: How To Identify Skin Cancer
Risk Of Getting Melanoma
Melanoma is more than 20 times more common in whites than in African Americans. Overall, the lifetime risk of getting melanoma is about 2.6% for whites, 0.1% for Blacks, and 0.6% for Hispanics. The risk for each person can be affected by a number of different factors, which are described in Risk Factors for Melanoma Skin Cancer.
Melanoma is more common in men overall, but before age 50 the rates are higher in women than in men.
The risk of melanoma increases as people age. The average age of people when it is diagnosed is 65. But melanoma is not uncommon even among those younger than 30. In fact, its one of the most common cancers in young adults .
How Is Skin Cancer Diagnosed In A Child
The healthcare provider will examine your child’s skin. Tell the healthcare provider:
-
When you first noticed the skin problem
-
If it oozes fluid or bleeds, or gets crusty
-
If its changed in size, color, or shape
-
If your child has pain or itching
Tell the healthcare provider if your child has had skin cancer in the past, and if other your family members have had skin cancer.
Your child’s healthcare provider will likely take a small piece of tissue from a mole or other skin mark that may look like cancer. The tissue is sent to a lab. A doctor called a pathologist looks at the tissue under a microscope. He or she may do other tests to see if cancer cells are in the sample. The biopsy results will likely be ready in a few days or a week. Your child’s healthcare provider will tell you the results. He or she will talk with you about other tests that may be needed if cancer is found.
Also Check: What Is Precancerous Skin Cancer
What Are Possible Complications Of Skin Cancer In A Child
Possible complications depend on the type and stage of skin cancer. Melanoma is more likely to cause complications. And the more advanced the cancer, the more likely there will be complications.
Complications may result from treatment, such as:
-
Loss of large areas of skin and underlying tissue
-
Scarring
-
Problems with the area healing
-
Infection in the area
-
Return of the skin cancer after treatment
Melanoma may spread to organs throughout the body and cause death.
What Does Skin Cancer Look Like
There are many different types of skin cancer . Each type looks different. Also, skin cancer in people with dark skin often looks different from skin cancer in people with fair skin. A change on the skin is the most common sign of skin cancer. This may be any new growth on the skin, a sore that doesn’t heal, or a change in an old growth.
If you notice a change on your skin, see your doctor. Don’t wait until the change looks like the more advanced skin cancers in these photos.
You May Like: Can You Live With Skin Cancer
What Causes Skin Cancer
Ultraviolet radiation from the sun is the number one cause of skin cancer, but UV light from tanning beds is just as harmful. Exposure to sunlight during the winter months puts you at the same risk as exposure during the summertime.
Cumulative sun exposure causes mainly basal cell and squamous cell skin cancer, while episodes of severe blistering sunburns, usually before age 18, can cause melanoma later in life. Other less common causes are repeated X-ray exposure, scars from burns or disease, and occupational exposure to certain chemicals.
Ultraviolet A and Ultraviolet B rays also affect the eyes and the skin around the eyes. Sun exposure may lead to cataracts, cancer of the eyelids, and possibly macular degeneration.
Key Points About Skin Cancer In Children
-
Skin cancer is rare in children.
-
Skin cancer is more common in people with light skin, light-colored eyes, and blond or red hair.
-
Follow the ABCDE rule to tell the difference between a normal mole and melanoma.
-
Biopsy is used to diagnose skin cancer.
-
Skin cancer can be treated with surgery, medicine, and radiation.
Staying out of the sun is the best way to prevent skin cancer.
Read Also: How Serious Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Can You Be Too Young For Melanoma
The most common type of cancer in the United States is not heart or lung cancer, but rather skin cancer. Skin cancers come in a variety of forms, and there are many different signs of skin cancer. But how young is too young to develop skin cancer, especially melanoma? Lets talk through the facts as well as what to keep an eye on.
How Young Is Too Young For A Child To Get Melanoma

Children CAN develop melanoma the deadliest type of tumor that can arise from a type of skin cell known as the melanocyte: a pigment producing cell.
There is no age that is too young to develop melanoma as a child, says Dr. Joel Schlessinger, MD, a dermatologist with a private practice in Omaha, NE.
In my practice I have seen melanoma in many young patients and have one 17-year-old who nearly needed to have an amputation due to melanoma of the toe.
Whats with the increase in melanoma cases in younger and younger people, including children?
This seems to contradict our evolutionary biology after all, ancient man spent hours every day smack in the sun, before umbrellas, tents, wide-brimmed hats and sunglasses were invented.
Researchers point to the intermittency of sun exposure as a risk factor for melanoma.
Intermittent blasts of sun exposure shock the DNA and damage it, causing changes that can, over time, give rise to melanoma.
Dr. Schlessinger continues, Sadly, we are now seeing a huge spike in melanoma cases due to indoor tanning and the trend of tanning before proms, weddings and all other events.
Additionally, damage to the skin as well as moles is being done on a daily basis when going to tanning booths.
Tanning booths are not safer than the sun in fact, their dose of radiation is much more concentrated, which is why you can get burned in just five minutes.
Moles that are present since birth are more likely to develop melanoma, says Dr. Schlessinger.
Read Also: What Is Grade 3 Invasive Ductal Carcinoma