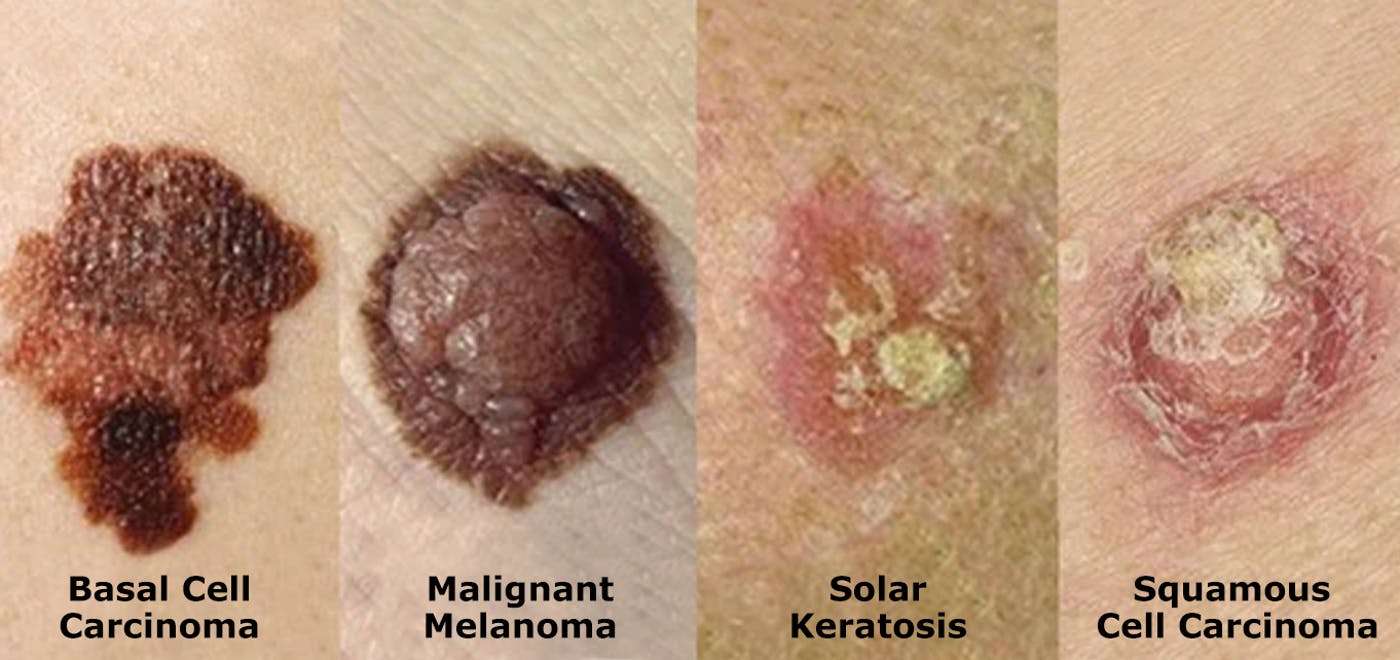
Cancerous: Basal Cell Carcinoma
What it is: Basal cell carcinomas are usually found on sun-exposed areas, such as the face and neck. They also tend to grow so slowly that they rarely cause any harm.
What it looks like: According to Dr. Rosen, basal cells look like a raised bump on the skin or a red scaly patch that doesnt go away. How its treated: Some basal cell carcinomas can be treated with a cream thats applied daily for several weeks, while others are below the surface and need to be surgically removed. Basal cell carcinoma is really curable, says Dr. Rosen, but it can leave you with a scar that can be quite noticeable.
What Melanoma Looks Like
Melanoma is a skin disease affecting approximately 132,000 people globally each year. While it is the rarest form of skin cancer, it is also the deadliest. Thats why knowing what it looks like is key to catching it early and preventing it from spreading deeper into the body. Below we go over the common symptoms of melanoma so you can know how it looks and what you should watch out for on your skin. Below are some melanoma and skin cancer pictures so you know what to look out for.
How Do People Find Signs Of Melanoma On Their Own Skin
Performing a skin self-exam as often as recommended by your dermatologist is the best way. While examining your skin, you want to look for the following:
-
Mole that is changing in any way
-
Spot that looks different from the rest of the spots on your skin
-
Growth or spot on your skin that itches, bleeds, or is painful
-
Band of color beneath or around a nail
-
Sore that doesnt heal or heals and returns
The ABCDEs of melanoma can help you find changes to a mole, freckle, or other spot on your skin.
Recommended Reading: Does Insurance Cover Skin Cancer Screening
What Are The Symptoms Of Skin Cancer
Talk to your doctor if you notice changes in your skin such as a new growth, a sore that doesnt heal, a change in an old growth, or any of the A-B-C-D-Es of melanoma.
A change in your skin is the most common sign of skin cancer. This could be a new growth, a sore that doesnt heal, or a change in a mole.external icon Not all skin cancers look the same.
For melanoma specifically, a simple way to remember the warning signs is to remember the A-B-C-D-Es of melanoma
- A stands for asymmetrical. Does the mole or spot have an irregular shape with two parts that look very different?
- B stands for border. Is the border irregular or jagged?
- C is for color. Is the color uneven?
- D is for diameter. Is the mole or spot larger than the size of a pea?
- E is for evolving. Has the mole or spot changed during the past few weeks or months?
Talk to your doctor if you notice changes in your skin such as a new growth, a sore that doesnt heal, a change in an old growth, or any of the A-B-C-D-Es of melanoma.
What Is The Follow
Most skin cancer is cured surgically in the dermatologist’s office. Of skin cancers that do recur, most do so within three years. Therefore, follow up with your dermatologist as recommended. Make an appointment immediately if you suspect a problem.
If you have a more deeply invasive or advanced malignant melanoma, your oncologist may want to see you every few months. These visits may include total body skin examinations, regional lymph node checks, and periodic chest X-rays. Over time, the intervals between follow-up appointments will increase. Eventually these checks may be done only once a year.
Read Also: Does Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
Less Common Skin Cancers
Uncommon types of skin cancer include Kaposi’s sarcoma, mainly seen in people with weakened immune systems sebaceous gland carcinoma, an aggressive cancer originating in the oil glands in the skin and Merkel cell carcinoma, which is usually found on sun-exposed areas on the head, neck, arms, and legs but often spreads to other parts of the body.
Amelanotic Melanoma: It Doesnt Look Like Other Melanomas
Odds are, if you have spent time on SkinCancer.org, you know the classic ABCDE warning signs of melanoma: Asymmetry, Border irregularity, Color variations, Diameter over ¼ inch or Dark in color, and Evolution or change. But did you know that some melanomas have very different features?
For example, certain melanomas may have no color at all. Physicians refer to these as amelanotic melanomas, because they are conspicuously missing melanin, the dark pigment that gives most moles and melanomas their color. These unpigmented melanomas may be pinkish-looking, reddish, purple, normal skin color or essentially clear and colorless.
- An example of a flat, amelanotic, superficial spreading melanoma on the leg.
- A nodular melanoma developing within an amelanotic melanoma in situ on the scalp.
While these melanomas lack pigment, they may have other melanoma warning signs to stay on the lookout for, such as asymmetry and an irregular border. In addition, more and more physicians today stress the importance of the E in the ABCDEs evolution or change. The Skin Cancer Foundation recommends that you examine your skin head to toe every month, especially looking for any new mole or any sign of change in an existing mole. If you spot any change that you consider suspicious, see a skin specialist without delay.
To help you spot unusual melanomas, you can also use early recognition strategies beyond the ABCDEs, such as the Ugly Duckling sign.
Read Also: Osteomyoma
What Do Stage 4 Tumors Look Like
A change to an existing mole or normal skin can be the first sign that the cancer has spread. But the physical symptoms of stage 4 melanoma arent the same for everyone. A doctor will diagnose stage 4 melanoma by looking at the primary tumor, the spread to nearby lymph nodes, and whether the tumor has spread to different organs. While your doctor wont base their diagnosis only on what your tumor looks like, part of their diagnosis involves looking at the primary tumor.
What Is Melanoma Skin Cancer
Melanoma is a form of skin cancer, arising from cells within the skin called melanocytes.
These melanocytes are normally responsible for producing melanin, a dark coloured pigment which is responsible for giving our skin its colour and the formation of moles on the skin.
As with other forms of skin cancer, melanomas are linked to exposure to UV light. It is thought that your genetics may also have a role in whether you develop melanoma and there does appear to be a higher risk of skin cancers if other family members have also had skin cancer.
Some studies also suggest that those with many moles or pale skin that burns easily in the sun are also at an increased risk of melanoma.
In its initial stages, a melanoma begins by a concentrated overgrowth of melanocytes which start to accumulate. After this process has started, the melanocytes begin to spread to other layers of skin, and if undetected or ignored, can spread to other parts of the body . After being diagnosed, the melanoma will be staged depending on the extent of its growth.
Minimising your exposure to UV light is one simple way to reduce your risk of skin cancer. This can be by reducing your amount of time out in the sun as well as using a high SPF sunscreen.
Don’t Miss: Basal Skin Cancer Survival Rates
When To See A Doctor
It is always vital to seek medical advice early for a skin change, no matter how small it may appear. Make an appointment with your doctor for a skin exam if you notice:
- Any new changes, lesions, or persistent marks on your skin
- A mole that is asymmetrical, has an irregular border, is multicolored, is large in diameter, is evolving, or has begun to crust or bleed
- An “ugly duckling” mole on the skin
- Any changes to your skin that you are concerned about
Stay Alert Contact Your Doctor
The best way to catch melanoma early is by paying attention to your body and noticing any changes or new additions. It can be overwhelming to try to remember all of the symptoms, thats why if you think anything looks suspicious or just doesnt feel quite right, its best to contact your doctor immediately for a diagnosis.
Recommended Reading: Does Skin Cancer Burn And Itch
How To Check Yourself
By checking your skin regularly, you will learn to recognize what spots, moles, and marks are already present and how they typically appear. The more you get to know your skin, the easier it will be for you to detect changes, such as new lesions or spots and moles that have changed in shape, size, or color, or have begun bleeding.
It is best to use a full-length mirror when checking your skin for changes or early signs of skin cancer. Observe your body in the mirror from all anglesfront, back, and on each side.
Taking each part of the body in turn, start with your hands and arms, carefully examining both sides of the hands and the difficult to see places like the underarms. Move on to your legs and feet, making sure to check the backs of your legs, soles of your feet, and between your toes.
Use a small mirror to get a closer look at your buttocks and your back. You can also use a small mirror to examine your face, neck, head, and scalp. Don’t forget to part your hair and feel around your scalp.
Nail Melanoma Early Stages
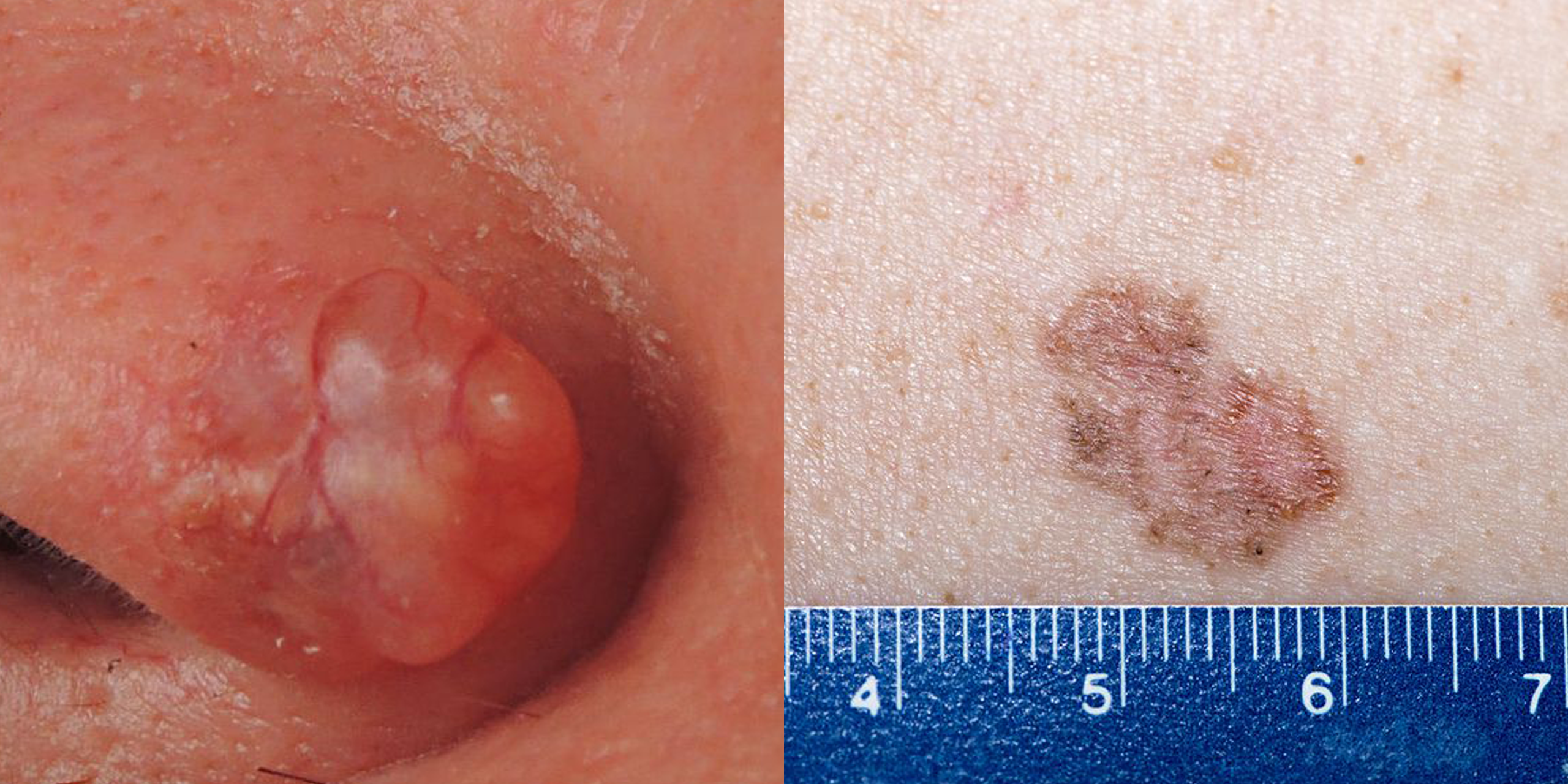
Melanoma, also redundantly known as malignant melanoma, is a type of skin cancer that develops from the pigment-producing cells known as melanocytes. Melanomas typically occur in the skin, but may rarely occur in the mouth, intestines, or eye .In women, they most commonly occur on the legs, while in men, they most commonly occur on the back.
You May Like: Stage 3 Basal Cell Carcinoma Survival Rate
Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Skin Cancers
Basal cell and squamous cell cancers are by far the most common skin cancers, and actually are more common than any other form of cancer. Because they rarely spread to other parts of the body, basal cell and squamous cell skin cancers are usually less concerning and are treated differently from melanoma. These cancers are discussed in Basal and Squamous Cell Skin Cancer.
Why Is Melanoma On The Rise
The main reason for the rise in deaths from melanoma since the 1970s is the UKs ageing population, Dr Bav Shergill previously told HuffPost UK.
However other factors such as increased affordability and availability of foreign holidays, the enduring fashion for tanned skin, and the popularity of sun beds also play a part. Figures show that if the cancer is caught early, 91% will survive the disease for five years or more.
Early detection is vital for successful treatment of skin cancer, said Dr Shergill.
People should not delay visiting their GP if theyre concerned about a potential skin cancer. It is a major source of concern that skin cancer referrals have dropped significantly during the Covid-19 pandemic.
Recommended Reading: Squamous Cell Carcinoma Skin Metastasis
What Are Symptoms Of Melanoma
Usually, the first sign of melanoma is a change in the shape, color, size, or sensation of an existing mole. The most important warning sign of melanoma is the appearance of new skin spots or blemishes that have changed in size, shape, or color. Any change in the size, shape, color, or height of the spots on the skin, or any new symptoms, such as bleeding, itching, or crusting, may be a warning sign of melanoma. Unusual moles, sores, bumps, blemishes, marks, or changes in appearance or sensation anywhere on the skin may be a sign of melanoma or other types of skin cancer, or a warning that you may want to do so.
Melanoma is often asymptomatic, but the first sign is usually a change in an existing mole or a new spot. Melanoma symptoms usually appear initially as changes in the appearance of the skin caused by changes in the way melanocytes are formed. Moles usually appear on healthy skin and are not necessarily an early sign of melanoma.
Most melanomas are black or brown, but some are pink, red, purple, or flesh-colored. About 30% of melanomas occur in existing moles, but the rest occur on normal skin.
Medical Treatment For Skin Cancer
Surgical removal is the mainstay of therapy for both basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas. For more information, see Surgery.
People who cannot undergo surgery may be treated by external radiation therapy. Radiation therapy is the use of a small beam of radiation targeted at the skin lesion. The radiation kills the abnormal cells and destroys the lesion. Radiation therapy can cause irritation or burning of the surrounding normal skin. It can also cause fatigue. These side effects are temporary. In addition, a topical cream has recently been approved for the treatment of certain low-risk nonmelanoma skin cancers.
In advanced cases, immune therapies, vaccines, or chemotherapy may be used. These treatments are typically offered as clinical trials. Clinical trials are studies of new therapies to see if they can be tolerated and work better than existing therapies.
Don’t Miss: Metastatic Basal Cell Carcinoma Survival Rate
How To Perform A Self
1. Examine your face
Especially your nose, lips, mouth and ears front and back. Use one or both mirrors to get a clear view.
2. Inspect your scalp
Thoroughly inspect your scalp, using a blow-dryer and mirror to expose each section to view. Get a friend or family member to help, if you can.
3. Check your hands
Palms and backs, between the fingers and under the fingernails. Continue up the wrists to examine both the front and back of your forearms.
4. Scan your arms
Standing in front of the full-length mirror, begin at the elbows and scan all sides of your upper arms. Dont forget the underarms.
5. Inspect your torso
What Causes Skin Cancer
Ultraviolet light exposure, most commonly from sunlight, is overwhelmingly the most frequent cause of skin cancer.
Other important causes of skin cancer include the following:
- Use of tanning booths
- Immunosuppression – This means impairment of the immune system. The immune system protects the body from foreign entities, such as germs or substances that cause an allergic reaction. This suppression may occur as a consequence of some diseases or can be due to medications prescribed to combat conditions such as autoimmune diseases or prevent organ transplant rejection.
- Exposure to unusually high levels of X-rays
- Contact with certain chemicals-arsenic , hydrocarbons in tar, oils, and soot
The following people are at the greatest risk:
- People with fair skin, especially types that freckle, sunburn easily, or become painful in the sun
- People with light hair and blue or green eyes
- Those with certain genetic disorders that deplete skin pigment such as albinism, xeroderma pigmentosum
- People who have already been treated for skin cancer
- People with numerous moles, unusual moles, or large moles that were present at birth
- People with close family members who have developed skin cancer
- People who had at least one severe sunburn early in life
A basal cell carcinoma usually looks like a raised, smooth, pearly bump on the sun-exposed skin of the head, neck, or shoulders.
A squamous cell carcinoma is commonly a well-defined, red, scaling, thickened patch on sun-exposed skin.
Read Also: Etiology Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Whats The Outlook For Stage 4 Melanoma
Once the cancer spreads, locating and treating the cancerous cells becomes more and more difficult. You and your doctor can develop a plan that balances your needs. The treatment should make you comfortable, but it should also seek to remove or slow cancer growth. The expected rate for deaths related to melanoma is 10,130 people per year. The outlook for stage 4 melanoma depends on how the cancer has spread. Its usually better if the cancer has only spread to distant parts of the skin and lymph nodes instead of other organs.
What Are The Melanoma Stages And What Do They Mean
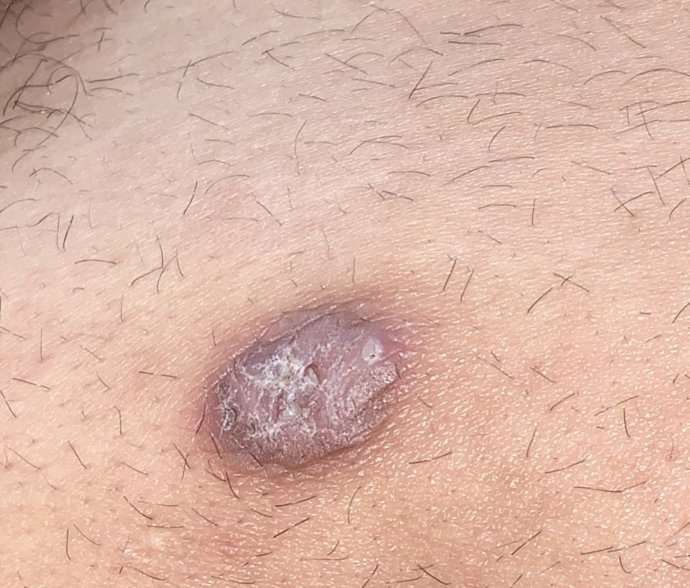
Early melanomas
Stage 0 and I are localized, meaning they have not spread.
- Stage 0: Melanoma is localized in the outermost layer of skin and has not advanced deeper. This noninvasive stage is also called melanoma in situ.
- Stage I: The cancer is smaller than 1 mm in Breslow depth, and may or may not be ulcerated. It is localized but invasive, meaning that it has penetrated beneath the top layer into the next layer of skin. Invasive tumors considered stage IA are classified as early and thin if they are not ulcerated and measure less than 0.8 mm.
Find out about treatment options for early melanomas.
Intermediate or high-risk melanomas
Localized but larger tumors may have other traits such as ulceration that put them at high risk of spreading.
- Stage II: Intermediate, high-risk melanomas are tumors deeper than 1 mm that may or may not be ulcerated. Although they are not yet known to have advanced beyond the primary tumor, the risk of spreading is high, and physicians may recommend a sentinel lymph node biopsy to verify whether melanoma cells have spread to the local lymph nodes. Thicker melanomas, greater than 4.0 mm, have a very high risk of spreading, and any ulceration can move the disease into a higher subcategory of stage II. Because of that risk, the doctor may recommend more aggressive treatment.
Learn more about sentinel lymph node biopsy and melanoma treatment options.
Advanced melanomas
Don’t Miss: Does Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
Can Changing My Diet Help Prevent Melanoma
The American Cancer Society advocates eating a plant-based diet over an animal-based diet as part of a healthy plan to avoid all cancers. Growing evidence suggests that plants pack a powerful punch in any fight against cancer because they’re nutritious, cholesterol-free and fiber-rich.
Theres no doubt that a healthy diet can protect your immune system. Having a strong immune system is important to help your body fight disease. Some research has shown that a Mediterranean diet is a healthy choice that may help prevent the development of cancer. Talk to your healthcare provider about the role food plays in lowering your cancer risks.
Some skin and immune-system healthy foods to consider include:
- Daily tea drinking: The polyphenols in tea help strengthen your immune system. Green tea contains more polyphenols than black tea.
- High vegetable consumption: Eating carrots, cruciferous and leafy vegetables is linked to the prevention of cutaneous melanoma.
- Weekly fish intake: Study participants who ate fish weekly seemed to avoid developing the disease when compared to those who did not eat fish weekly.